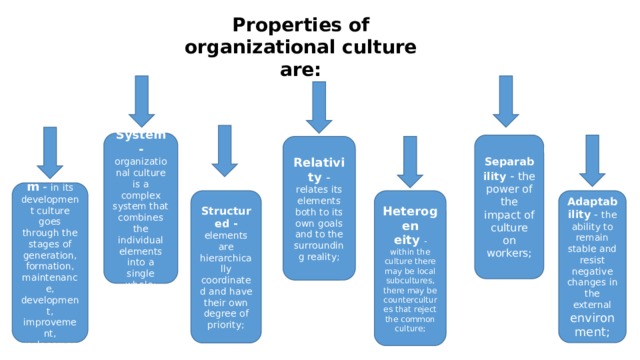
Properties of organizational culture are:
System - organizational culture is a complex system that combines the individual elements into a single whole;
Separability - the power of the impact of culture on workers;
Relativity - relates its elements both to its own goals and to the surrounding reality;
Dynamism - in its development culture goes through the stages of generation, formation, maintenance, development, improvement, replacement
Structured - elements are hierarchically coordinated and have their own degree of priority;
Adaptability - the ability to remain stable and resist negative changes in the external environment;
Heterogen
eity - within the culture there may be local subcultures, there may be countercultures that reject the common culture;

Principles of the formation of culture
- The principle of complexity of ideas about the purpose of the economic system of the organization, culture should reflect not so much the relationship between members of the organization, as the idea of the purpose of the organization as a whole;
- The principle of prioritization of the values and philosophy of the company. Before the formation of culture, values and philosophy must be formulated;
- The principle of historicity. Culture can not be easily manipulated, it develops over the years;
- The principle of denial of force. It is impossible to artificially impose a strong culture on a weak culture, and vice versa;
- The principle of comprehensive assessment. Evaluation of the impact of culture on the performance of the company should be based on an integrated approac

External adaptation and internal integration
The external environment has a significant impact on the organization, which naturally affects its culture. However, as practice shows, two organizations operating in the same environment may have very different cultures. This is because, through their collective experience, members of the organization solve two very important problems in different ways. The first is external adaptation: what and how should be done by the organization. The second is internal integration: how employees of the organization solve their daily problems related to their work and life in the organization.
Problems of external adaptation and survival are associated with the mission, strategy, goals, means that the organization uses. Problems of internal integration are associated with a common language, conceptual categories, group boundaries and criteria for entering and exiting groups, the ratio of power and status, the system of personal relationships, the ideology of the organization, the definition of desirable and undesirable behavior.
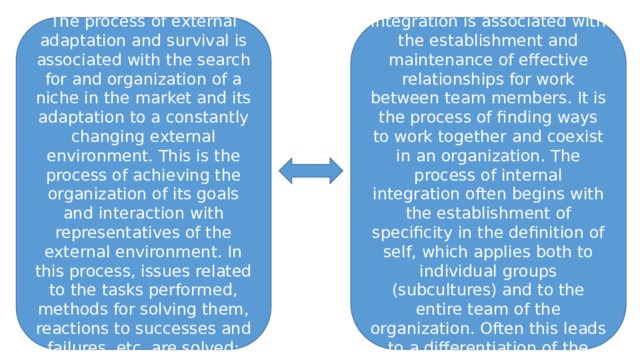
The process of external adaptation and survival is associated with the search for and organization of a niche in the market and its adaptation to a constantly changing external environment. This is the process of achieving the organization of its goals and interaction with representatives of the external environment. In this process, issues related to the tasks performed, methods for solving them, reactions to successes and failures, etc. are solved;
The process of internal integration is associated with the establishment and maintenance of effective relationships for work between team members. It is the process of finding ways to work together and coexist in an organization. The process of internal integration often begins with the establishment of specificity in the definition of self, which applies both to individual groups (subcultures) and to the entire team of the organization. Often this leads to a differentiation of the organization.

By implementing communicative interaction, the members of the group (team) strive to describe for themselves the organizational world around them. They may conclude that it is changing or stagnant, full of possibilities or dangers. So, people will go to innovations, if they believe that they can make important changes in the world around them and that what used to be dangerous, can now become an opportunity for change.
The formation of organizational culture, its content, individual parameters are influenced by factors of external and internal environment.
At all stages of an organization’s development, the management culture of its leader (his personal faith, values and style) can largely determine the organization’s culture. In a very large degree, the influence of a leader or founder of a company on the formation of a culture is manifested if it is a strong (strongly pronounced managerial culture) personality, and the organization is only being created.
Formation of the organization's culture is connected with the external environment for the organization: the business environment in general and in the industry, in particular; samples of national culture.
The organization’s acceptance of a certain culture can be related to the specifics of the industry in which it operates, with the speed of technological and other changes, with market characteristics, consumers, etc. It is known that companies with “high technology” industries have a culture that contains “innovative” values and faith "in change". However, this feature can manifest itself in different ways in companies of the same industry, depending on the national culture in which one company or another operates.
Analysis of the factors of organizational culture formation shows that the latter is the subject of development and changes throughout the life of the organization.
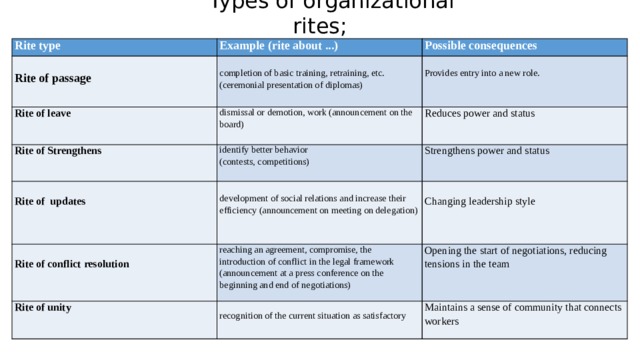
Types of organizational rites;
Rite type
Example (rite about ...)
Possible consequences
Rite of passage
Rite of leave
Rite of Strengthens
completion of basic training, retraining, etc.
dismissal or demotion, work (announcement on the board)
identify better behavior
Provides entry into a new role.
Reduces power and status
(ceremonial presentation of diplomas)
Strengthens power and status
Rite of updates
(contests, competitions)
development of social relations and increase their efficiency (announcement on meeting on delegation)
Rite of conflict resolution
reaching an agreement, compromise, the introduction of conflict in the legal framework (announcement at a press conference on the beginning and end of negotiations)
Rite of unity
Changing leadership style
Opening the start of negotiations, reducing tensions in the team
recognition of the current situation as satisfactory
Maintains a sense of community that connects workers
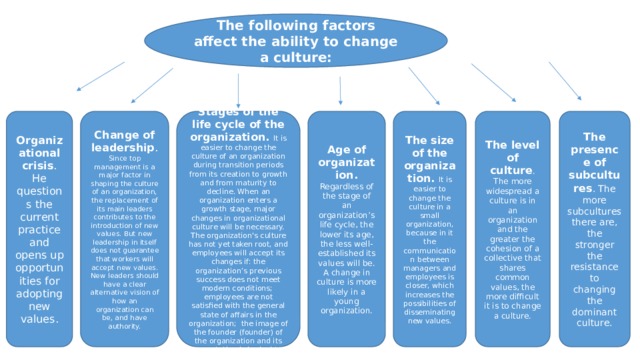
The following factors affect the ability to change a culture:
Organizational crisis . He questions the current practice and opens up opportunities for adopting new values.
Change of leadership . Since top management is a major factor in shaping the culture of an organization, the replacement of its main leaders contributes to the introduction of new values. But new leadership in itself does not guarantee that workers will accept new values. New leaders should have a clear alternative vision of how an organization can be, and have authority.
Age of organization. Regardless of the stage of an organization’s life cycle, the lower its age, the less well-established its values will be. A change in culture is more likely in a young organization.
Stages of the life cycle of the organization. It is easier to change the culture of an organization during transition periods from its creation to growth and from maturity to decline. When an organization enters a growth stage, major changes in organizational culture will be necessary. The organization's culture has not yet taken root, and employees will accept its changes if: the organization’s previous success does not meet modern conditions; employees are not satisfied with the general state of affairs in the organization; the image of the founder (founder) of the organization and its reputation is in doubt
The size of the organization. It is easier to change the culture in a small organization, because in it the communication between managers and employees is closer, which increases the possibilities of disseminating new values.
The presence of subcultures . The more subcultures there are, the stronger the resistance to changing the dominant culture.
The level of culture . The more widespread a culture is in an organization and the greater the cohesion of a collective that shares common values, the more difficult it is to change a culture.

Methods of managing resistance when changing organizational culture .
Informing and communicating. One of the most common ways to overcome resistance to the implementation of a strategy is to pre-inform people. Getting an idea of the upcoming strategic changes helps to realize the need for these changes and their logic. The information process can include one-on-one discussions, group workshops or reports.
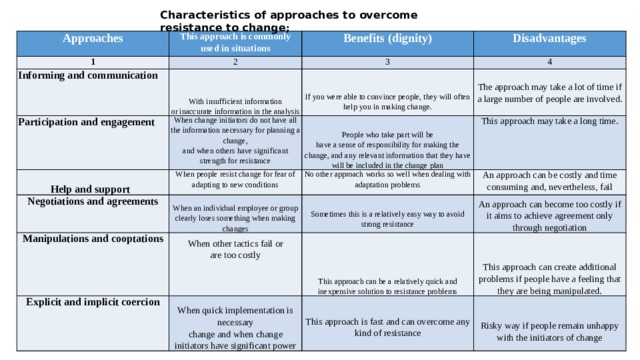
Characteristics of approaches to overcome resistance to change ;
Approaches
This approach is commonly used in situations
1
Benefits (dignity)
2
Informing and communication
Disadvantages
3
With insufficient information
Participation and engagement
Help and support
4
or inaccurate information in the analysis
If you were able to convince people, they will often help you in making change s.
When change initiators do not have all the information necessary for planning a change,
When people resist change for fear of adapting to new conditions
Negotiations and agreements
The approach may take a lot of time if a large number of people are involved.
People who take part will be
and when others have significant strength for resistance
have a sense of responsibility for making the change, and any relevant information that they have will be included in the change plan
This approach may take a long time.
Manipulations and cooptations
When an individual employee or group clearly loses something when making changes
No other approach works so well when dealing with adaptation problems
Sometimes this is a relatively easy way to avoid strong resistance
An approach can be costly and time consuming and, nevertheless, fail
Explicit and implicit coercion
When other tactics fail or
are too costly
When quick implementation is necessary
An approach can become too costly if it aims to achieve agreement only through negotiation
This approach can be a relatively quick and inexpensive solution to resistance problems
This approach is fast and can overcome any kind of resistance
change and when change initiators have significant power
This approach can create additional problems if people have a feeling that they are being manipulated.
Risky way if people remain unhappy with the initiators of change

Participation and engagement. If “strategists” involve potential opponents of the strategy at the planning stage, then they can often avoid resistance. In an effort to get involved in the implementation of strategic changes, their initiators listen to the opinions of employees involved in this strategy, and subsequently use their advice.
Assistance and support can be provided as providing opportunities for learning new skills, free time for employees to learn, just being heard and receiving emotional support. Help and support are especially needed when fear and anxiety are at the heart of resistance.
Negotiations and agreements. Negotiations are particularly appropriate when it is clear that someone is losing as a result of the change, but nonetheless has a significant resistance force.
Manipulations and cooptations. In some situations, managers try to hide their intentions from other people using manipulations. Manipulations in this case involve the selective use of information and the conscious presentation of events in a certain order advantageous to the initiator of the changes. One of the most common forms of manipulation is co-optation. Co-opting a person means giving her the desired role in planning and implementing change
Explicit and implicit coercion. Managers often overcome resistance to organizational change through coercion. Basically, they force people to come to terms with strategic changes by covert or overt threat (threatening job loss, promotion opportunities, etc.), or by real dismissal, or by transferring to lower-paying jobs.