УДК: 371.6: 911.3
Abdurakhmonov B.M.
Lecturer at the Department of Geography, NamSU
Uzbekistan, Namangan
FORMATION OF GEOGRAPHIC CULTURE THROUGH THE COMPLEX OF LEARNING TOOLS
Abstract: the article describes the scientific approach of the study, gives a classification of geography teaching tools, outlines the methodology for the formation of geographic culture through teaching tools, and draws a conclusion based on the results of the work done.
Key words: Geographic culture, scientific and pedagogical process, classifications of teaching aids, content of geographic education, attitude to the environment, the level of geographic culture.
Geographic culture is one of the three components of the concept of sustainable development, that is, economic development, social development and the ability to synthesize environmental responsibility as one of the qualities of an educated, enterprising and creative person, which allows us to consider the spirituality and morality of an individual at the level of relationships between nature and society. The formation of the geographical culture of mankind is a way of harmonizing interaction aimed at preserving the planet Earth, rational socio-economic activity of society and understanding the "nature - society" system.
Geography education is a scientific and pedagogical process aimed at acquiring geographic knowledge, abilities, skills and competencies, creative power and internal potential of students, acquiring values and developing skills for independent learning. The introduction of geographical education into pedagogical practice is carried out through the methodology of geographical education, which is the study of the system and technologies of geographical education. A special role in this process is played by the means of teaching the subject of geography. [5].
There is no clear, uniform and invariable classification of teaching aids; their classification can be approached for various reasons. (Рис.1).
Fig. 1. Classification of geography teaching aids
Based on different approaches and classifications, we have classified all learning tools and conditionally identified traditional and modern tools.
Teaching aids on physical geography are one of the important and necessary conditions for the implementation of the content of education, upbringing and student development of schoolchildren. An important aspect of educational tools is that they are used together and never deny each other. The teacher's task is to be able to select and apply effective teaching tools to enhance the learning process [1].
The complex of means of geographic education is considered: natural and specially prepared objects or objects of the environment, i.e. natural and artificial geographic objects used as a means of transferring educational information from a teacher to students in the school environment, as well as technical equipment included in the educational process for the student's assimilation of the content of geographic education and the acquisition of geographic culture.
The essence of the concept "Geographical culture" was first widely studied by the Russian scientist V.P. Maksakovskiy. Describing modern school geography, the scientist draws attention to the fact that the trend in the development of world reforms in education is based on the concept of cultural studies, reveals the essence of the cultural approach to education. He emphasizes that modern educational programs in geography are based on geographic culture. In his opinion, geographical culture includes the following components: 1) the geographical picture of the world; 2) geographical thinking; 3) methods of geography; 4) the language of geography [4].
These components of the geographical culture of the student's personality form the content of education in physical geography: 1) physical and geographical knowledge; 2) physical and geographical skills and abilities; 3) experience of physical and geographical creative activity; 4) the experience of an emotional-value attitude towards the environment in accordance with the mixed structure of their variability.
Physical geography teaching tools are man-made objects and environmental objects used in the educational environment (process) as a means of interaction between a teacher and a student, as a carrier of educational information to achieve the goal of physical-geographical education and the formation of a student's geographically cultural personality. The most optimal set of means for teaching physical geography is a set of interrelated forms and methods of teaching physical geography that do not duplicate each other, but, on the contrary, contribute to increasing the pedagogical potential of each individual element. Depending on the characteristics of the impact on students, complexity and origin, they are divided into natural, volumetric, graphic, symbolic, audio and multimedia means, in a broad sense, means for organizing and managing the process of teaching physical geography.
The methodology of using a complex of physical geography teaching aids in the formation of the geographical culture of students should be convenient, flexible and creative. Therefore, the main attention was paid to the methodology of increasing the level of formation of students' physical and geographical knowledge, abilities, skills and competencies, built on the basis of the principle from simple to complex, and the organizational and methodological structure of an integral methodological system of physical and geographical education was improved, aimed at the formation of students students of geographic culture through the use of appropriate teaching aids. We believe that the results and quality of education will be effective if an innovative methodological system based on technologies and teaching aids in physical geography is formed. To do this, we widely used the modeling method and followed the principle of the systems approach [3].
In order to study the state of the formation of geographic culture in the process of teaching physical geography, and in order to study and analyze the use of teaching aids, which are an integral part of the educational process, lessons and extracurricular activities in the subjects of natural history and geography in schools were observed. The level and provision of educational and methodological documentation of educational institutions was studied, interviews were conducted with teachers and students. Initially, the survey was conducted to study the pedagogical and methodological conditions of the process of teaching physical geography. [2].
Also, work was carried out to identify opportunities, problems, criteria, indicators and levels of formation of the geographical culture of students. On the basis of these criteria, the levels of geographic culture formation among students were determined. Based on this, the levels were divided into three: unsatisfactory, sufficient and high. The levels of geographic culture formation among students were determined on the basis of the above criteria based on the difference in indicators in the initial and final experimental work..
The general results of quantitative analysis for experimental schools are presented (Table 1).
Table 1.
The level of students' geographic culture at the beginning and at the end of experimental and test work
|
№ |
Group | levels |
| At the beginning | At the end |
| High | Enough | Unsatisfactory. | High | Enough | Unsatisfactory. |
| 1 | Experimental group (n1 =168 person.) | 23 | 57 | 88 | 89 | 54 | 25 |
| 2 | Control group (n2 =168 person.) | 15 | 54 | 99 | 13 | 69 | 86 |
In order to compare the data in the above table, we will form a diagram (see Fig. 1).
As can be seen from the diagram, since the upper and average indicators in the experimental group are higher than those in the control group.
The results obtained at the end of the experimental work confirm the reliability of the final conclusion, reflecting the increase in the level of the geographic culture of the personality of students in the middle general education school, the effectiveness of experimental work.
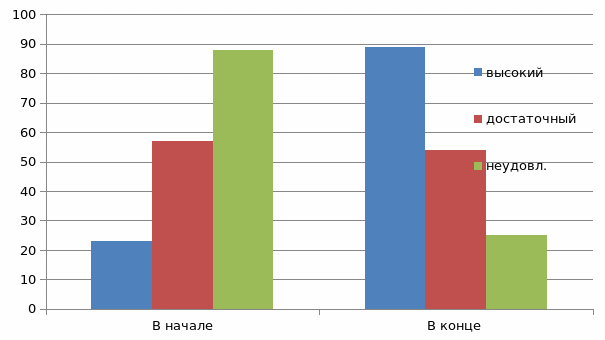
Fig. 1. The degree of mastery of the geographical culture of students based on the results of experimental and control works
This indicates the correct organization of experimental work, as well as the correct conduct of the research.
Conclusions:
▪ In the process of teaching physical geography, a set of indicators was developed that reflect the criteria for the formation of the geographical culture of students and their content:.
▪ The methodology developed to improve the process of teaching geography, that is, the systematic organization of the use of teaching aids, has a direct impact on the complex formation of all components of the geographical culture in students and the results obtained from the results of the experimental work confirmed the validity of the final conclusion on the increase in the level of the geographical culture of the personality of students..
Referens:
Andy Leeder. 100 Ideas for teaching geography. The tower Building. London-New York. 2006. – Р. 142.
Исаченко А. Г. Теория и методология географической науки: Учеб. для студ. - М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2004. –С. 400.
Лодатко, Е. А. Моделирование педагогических систем и процессов: монография / - Славянск: СГПУ. 2010. –С. 148.
Максаковский В.П. Географическая культура: учебное пособие для студентов вузов. – М.: Гуманит. Изд. Центр ВЛАДОС.- 1998. – С. 416.
Родзевич Н.Н. Географическая и экологическая культура. География в школе. 1999. №3. – С. 43.























